Sleep Quiz
- Overall are you satisfied with the amount and quality of your sleep? (Y/N)
- Do you watch television, work, or use your phone in bed? (Y/N)
- Do you go to bed and wake up at a similar time each evening (within 30 minutes)? (Y/N)
- Do you get outside for at least 20 minutes each day? (Y/N)
- Do you stay awake all day without dozing off OR taking a nap? (Y/N)
- Do you spend less than 30-minutes awake each night (including initial time to fall asleep and after awakening from a period of sleep)? (Y/N)
- Do you hit the snooze button more than 1 time in the morning? (Y/N)
- Do you wake up feeling rested during the average work day (Monday-Friday) (Y/N)
- Do you feel that your sleep quality impacts other areas of your life? (Y/N)
- On most days, do you have enough energy to complete your daily tasks? (Y/N)
- Do you take any sleeping medications OR other drugs prior to bed to help you fall asleep or stay asleep? (Y/N)
The Connection between Sleep and Pain
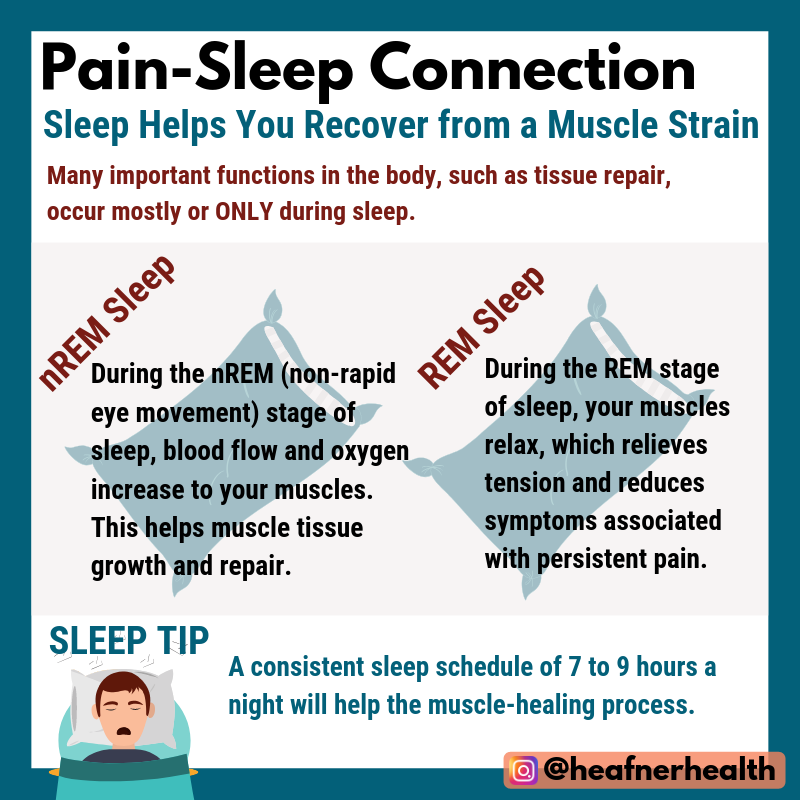
Humans must sleep! While there are numerous reasons for sleep, the most basic and all encompassing reason is to maintain balance among all of the systems in the body.
Not surprisingly, sleep complaints are present in 67-88% of chronic pain disorders.
|
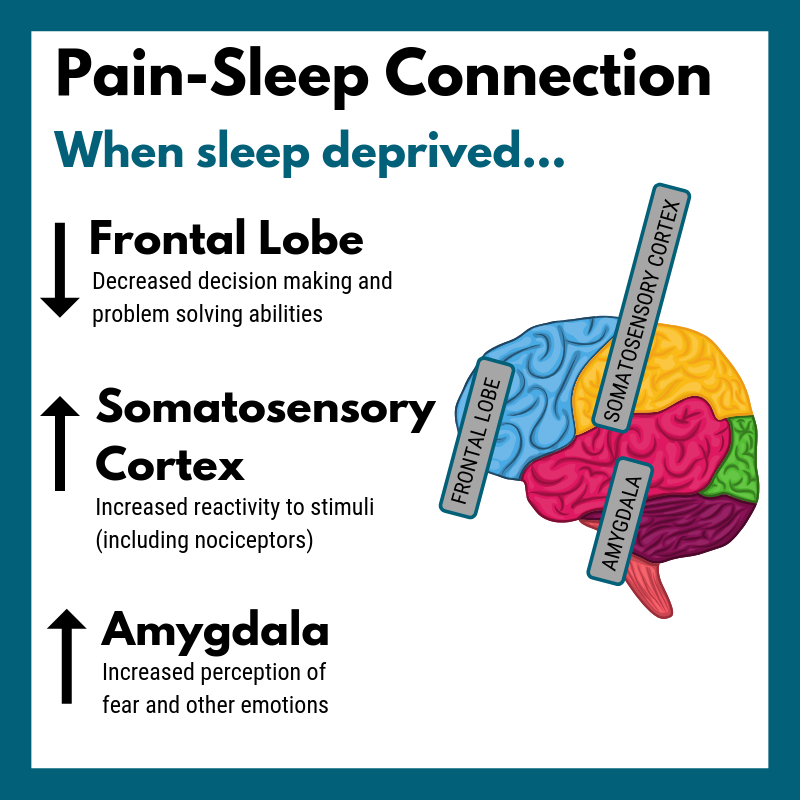
Two other key areas in the brain that help process pain are the striatum and insula. Interestingly, these two regions of the brain had a 60-90% decrease in activity with sleep deprivation. For example, if you are sleep deprived and get a paper cut at work, your brain may over-react to the cut because the insula and striatum are struggling to process severity of the cut.
This impacts key hormones in the brain, primarily dopamine, serotonin, and cortisol. Each of these hormones impact mood, thought processes, and overall energy levels.
|
Poor Sleep Can Impact Many Areas of your Life:
|
Poor Sleep Impacts Your Health
|
Sleep Health Definition:
Sleep health is a multidimensional pattern of sleep-wake-fulness, adapted to individual, social, and environmental demands, that promotes physical and mental well-being. Good sleep health is characterized by subjective satisfaction, appropriate timing, adequate duration, high efficiency, and sustained alertness during waking hours.
Sleep health is a multidimensional pattern of sleep-wake-fulness, adapted to individual, social, and environmental demands, that promotes physical and mental well-being. Good sleep health is characterized by subjective satisfaction, appropriate timing, adequate duration, high efficiency, and sustained alertness during waking hours.
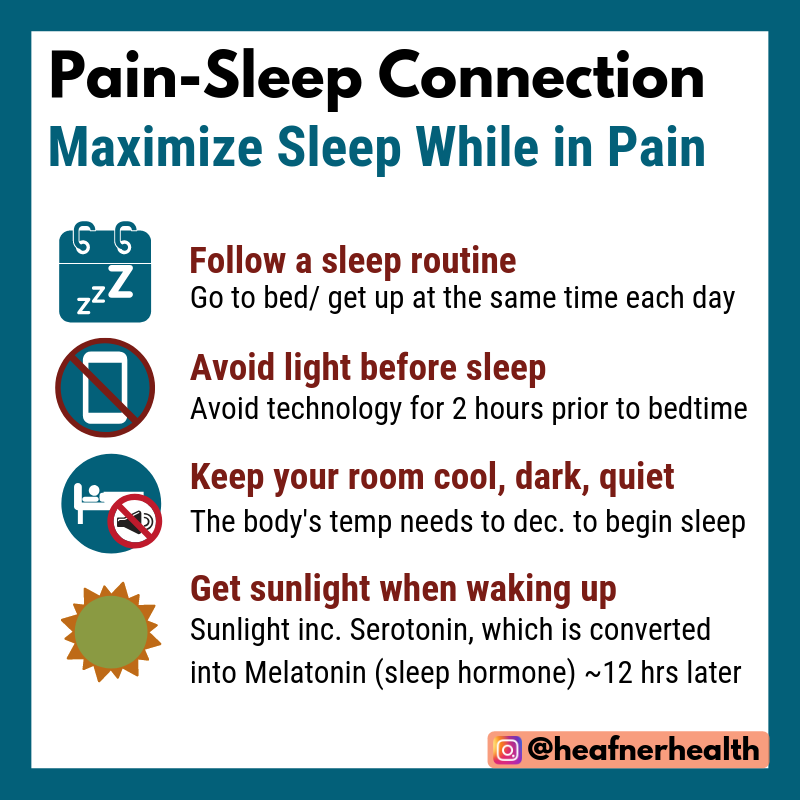
Sleep Advice and Recommendations
Questions to Ask Yourself:
- What do you do during the 2 hours before bedtime each night?
- From the question above, do you think any of these activities impact your sleep?
Tips to Help Change Your Sleep Habits
Routine is Key: What Does Your Sleep Routine Look like?
|
If you have tried the above techniques, learn about Stimulus Control Therapy
A poor sleep pattern likely has a series of negative cues and associations that are keeping you from a good night of sleep.